Rails Views with multiple assocations
I am learning how to create and handle Rails ActionViews with multiple associations. There are many ways to handle associations in rails and I have not seen a consistent use of one paradigm. It is a challenge to think through which model should be saved first, what associated data may already be in the database that you can use option_from_collection_for_select or the fields_for method, or determine which view to modify to bring in the association.
The key component is learning which model will load the most tables when performing the save action @model.save when handling multiple tables because of associated models.
Many-to-Many Example
For example, if you save the join table1 model, then the model’s save action will commit in one database transaction 3 inserts when save is performed:
- Insert into a table that a has_many reference to the join table.
- Insert into a table that has the second has_many reference to the join table.
- Finally, the join table will insert the “connection or join” references.
Contrast this to saving each model separately, it is a lot of work (many instance variables), but it also introduces potential database inconsistencies.
By saving and committing 3 transactions in one transaction, you will avoid any database errors if you were to manually perform a @model.save on three separate variables independently. There could be a potential database inconsistency should one of the inserts fails to save.
Params Hashs
At the end of the day, params is a hash.2 The params can include any values you set in the view. You must expect, require and permit them of course. You just have to use create a symbol in the view and expect it in the controller and you can create as many model objects as required.
For example, here’s how to set a symbol as a :tag.
<%= form.text_field :tag %>
Then you can pick up this value by setting the expect method your field like
params.expect(model: [:tag])
in your controller and assign it to your model object in your controller and save to your data base.
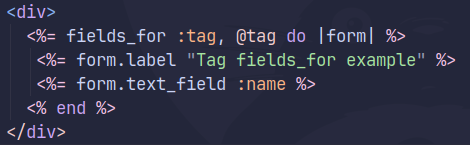
fields_for method
Method parameters: (record_name, record_object = nil, fields_options = nil, &block)
The fields_for creates a scope around a model with form_with, but doesn’t create form tags. So we can use this method to create additional model objects in the same form.3
The fields_for method is great for specific objects outside of the main object form_with function. I tried it out today, and it seems to make the most sense to bring associated models into the controller.
https://api.rubyonrails.org/v8.0.1/classes/ActionView/Helpers/FormBuilder.html#method-i-fields_for
